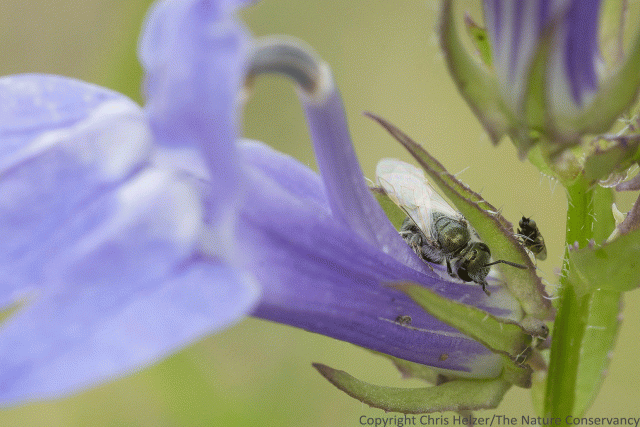
About a century ago, there were lots of reports of migrating insects along the East Coast of North America. Among those were numerous sightings of large, apparently migratory congregations of flies. And then, for reasons no one seems able to explain, there is nothing about North American fly migration in the scientific literature for almost 100 years.
WHAT HAVE WE BEEN DOING THAT’S MORE IMPORTANT THAN FOLLOWING UP ON REPORTS OF MIGRATORY FLIES??
It’s unconscionable, really. There are flies. Migrating long distances. And no one thought to go out and learn more about this?
Ok, that’s not fair. There’s been some great work in Europe on migratory flies (and other insects) – much of it in topographic locations like mountain passes where flying migrants of many kinds are funneled through narrow locations. They’ve documented numerous fly species, especially in the family Syrphidae (hover/drone flies), making seasonal flights in huge numbers. There’s still an awful lot to learn, but at least they’ve made a good start.
What’s especially frustrating is that some of those same migratory fly species are here in North America, too, along with many other close relatives. If they’re migratory in Europe, they’re almost surely migratory here, right? So why has no one checked?
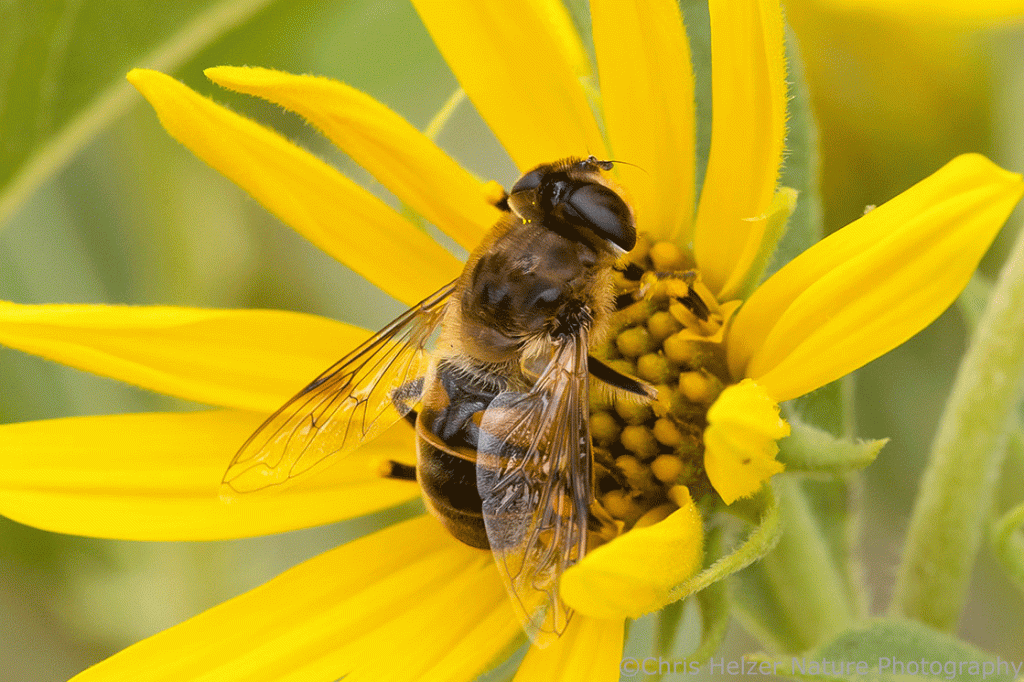
Well, after the long, inexplicable century of ignoring this fabulous field of research, there have finally been two recent North American studies (One in California and one in Illinois) on the topic. Both have confirmed that flies do still migrate on this continent, but we still know almost nothing about which species migrate, where they go, and why. Let’s fix this!
In the meantime, while we don’t know much about fly migration here in North America – and have huge knowledge gaps in Europe and elsewhere – we can at least marvel at it. First of all, as is the case with most migratory species on our continent, fly migration is probably a way to escape cold temperatures in the winter and then to spread out (and escape competition) when temperatures are moderate. Birds aren’t the only animals cool enough to do this, no matter what snooty ornithologists will tell you.
(I don’t mean to imply that all ornithologists are snooty. In fact, many are surprisingly decent and nice to talk to. If an ornithologist was snooty, though, they’d surely be braggy about bird migration, wouldn’t they?)

It appears that within at least many fly species, part of a population migrates south for the winter and the other part doesn’t. This is common among other insect groups as well. It’s a good way to hedge bets. If the subpopulation that stays put is wiped out by a particularly nasty winter, the migratory party can return and keep the species going. Or, if the migrants all die during their perilous journey, the ones who stayed home will persist.
How does an individual fly know if it’s supposed to migrate or hunker down for the winter? GEE, WOULDN’T IT BE GREAT IF WE KNEW SOMETHING ABOUT THAT??
Generally speaking, the assumption is that fly migration is a multi-generational phenomenon. The flies that head south in the winter have babies that then start the northward migration the following spring. By summer, either those progeny or their offspring will return to where their parents/grandparents had been the previous year. Of course, we don’t really know that BECAUSE NO ONE IS PAYING ATTENTION.
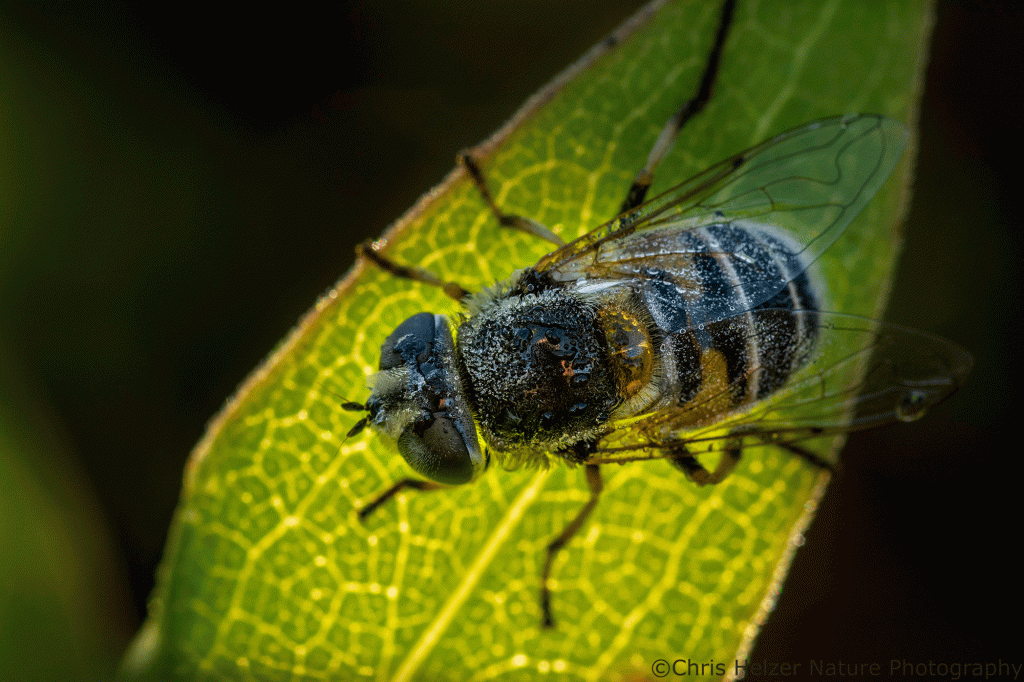
I’d love to continue this incredible, compelling story and provide lots more details. Unfortunately, as you might have gathered by now, we scientists have largely wasted a century doing less important work than fly migration research. As a result, I’ll just stop here.