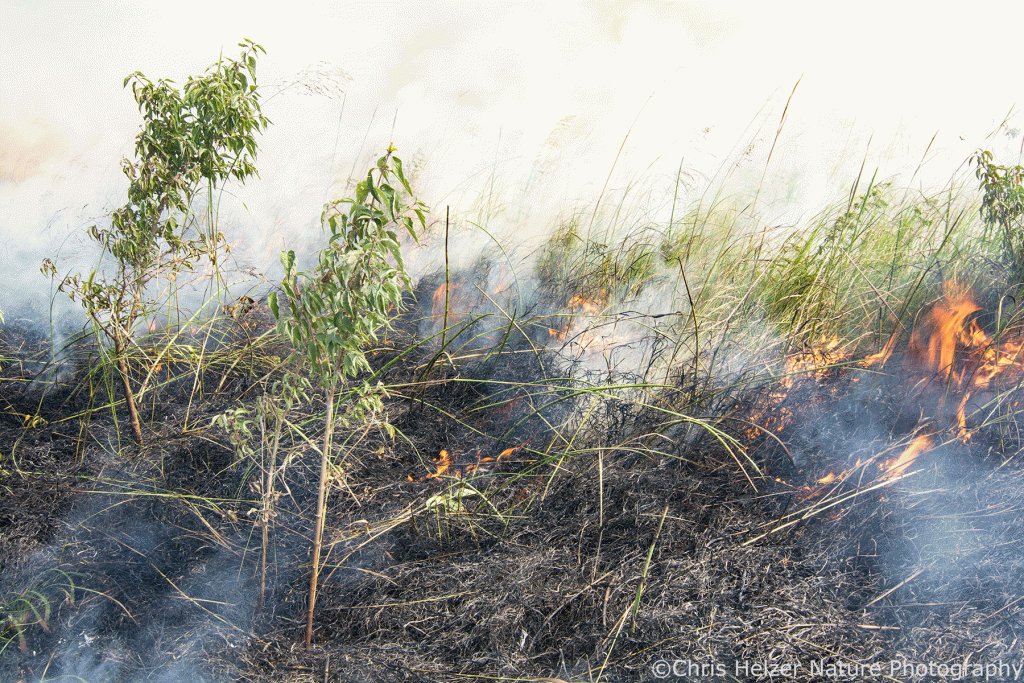In Part 1 of this topic, I wrote about the uncomfortable situation many prairie stewards find ourselves in – that our grasslands are getting “shrubbier” and it’s increasingly difficult to prevent that. Because the drivers for that change are mostly beyond our control, it seems obvious that we need to start thinking differently about grassland management.
There are still plenty of grasslands where we should work to prevent woody encroachment. However, there are also a lot of prairies where trees or shrubs have already become part of the community. In many other places, it appears to be just a matter of time. It seems smart for us to try to get ahead of this and figure out how to manage woodier grasslands for biodiversity and productivity.
Most of us haven’t focused much on how to manage the height and density of shrubs in our prairies because we’ve been thinking mostly about how to repel them. That means we need to start experimenting, and quickly. My team has implemented a couple different field trials in the last couple years and I’m going to share some preliminary results with you. I hope those results will spur others to share their experiences and, more importantly, ramp up their own experimentation efforts.
Our first trials focus on clonal deciduous shrubs (smooth sumac and rough-leaved dogwood). We started with the hypothesis that if we could hit them twice (or more) in the same growing season, we might get multiple years of suppressed height and density as a result. This hypothesis was informed by helpful conversations with people like Dean Kettle at the Kansas Biological Survey and several others.
Field Trial #1 – Smooth Sumac at The Nature Conservancy’s Niobrara Valley Preserve
In 2023, we treated a number of smooth sumac patches with treatments (often in combination) that included prescribed fire, mowing, and a non-lethal “burn-down” herbicide. The photos shown here illustrate what those sumac patches looked like on June 16, 2025.
Quick summary of preliminary results:
- Mowing sumac in June and August really reduced both the height and density of stems, and that impact has persisted for at least 2 years.
- An August mowing, followed by a dormant season fire (November, in our case), showed pretty similar results.
- June mowing followed by herbicide in August seemed slightly less effective than the above two treatments, but much better than any single treatment alone.
- June mowing followed by a November fire was the least effective of all the combinations listed so far, but still better than a single mowing treatment.
- All single treatment applications (June mowing, August mowing, November fire) showed quick recovery within two years.

Treatments were applied on June 13, August 9, and November 29, 2023. The photos below show sumac patches with various treatment combinations.
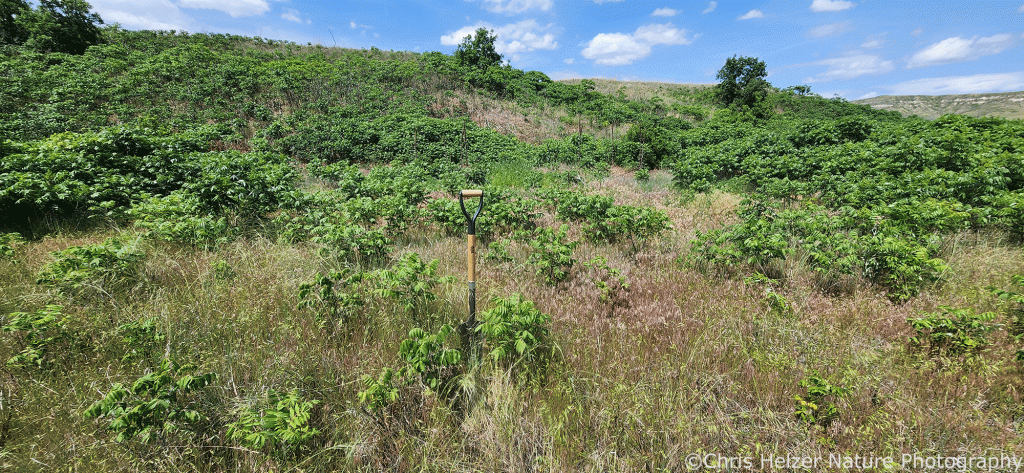
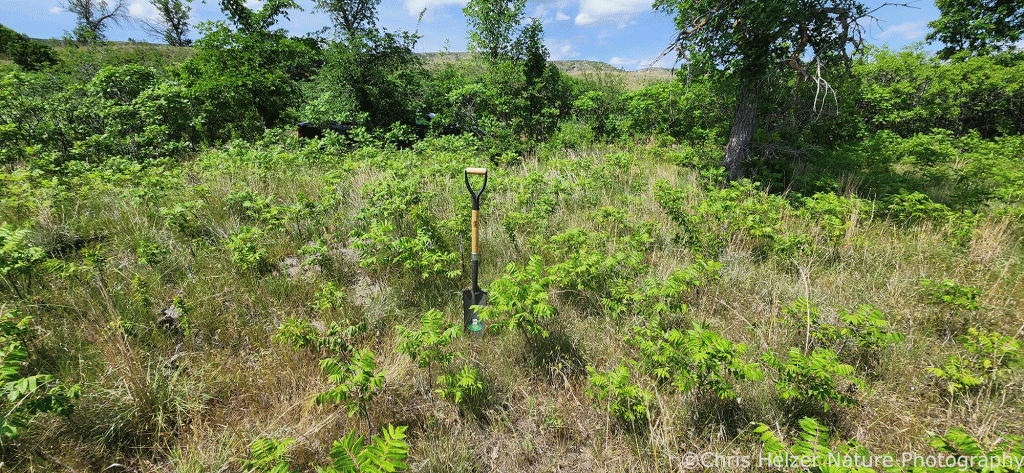
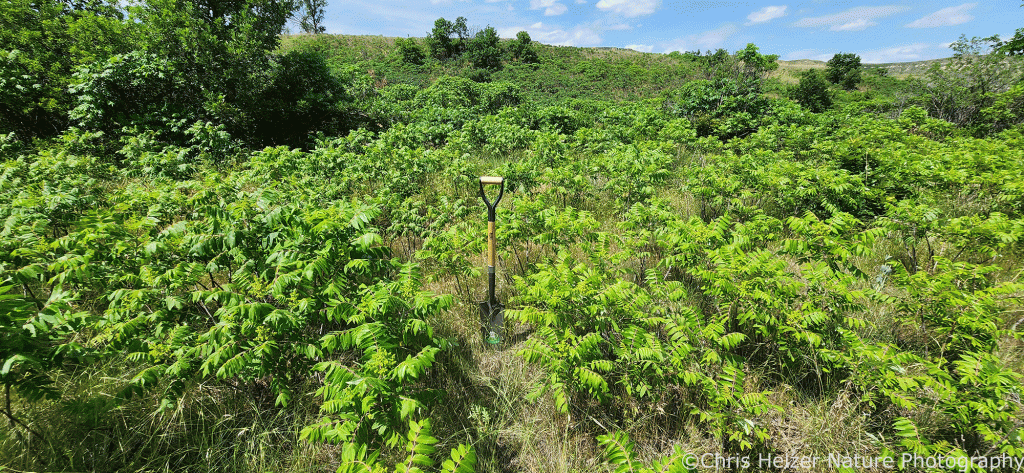
The herbicide we used contained the active ingredient Carfentrazone-ethyl, which disrupts cell membranes in leaves and essentially defoliates plants. The hope was that it would act much like a prescribed fire – injuring the shrubs without killing them or any surrounding plants. We mixed 17.5 ml (0.7 ml/gal) of AIM herbicide and 47.5 oz (1.9 oz/gal) of crop oil in 25 gallons of water and applied a heavy foliar spray.
We tested this on full-sized sumac plants in June, but the spray didn’t penetrate the canopy well, and only burned up the top layer of leaves. It seemed to work much better in August as a follow-up treatment to resprouted sumac plants mowed in June.
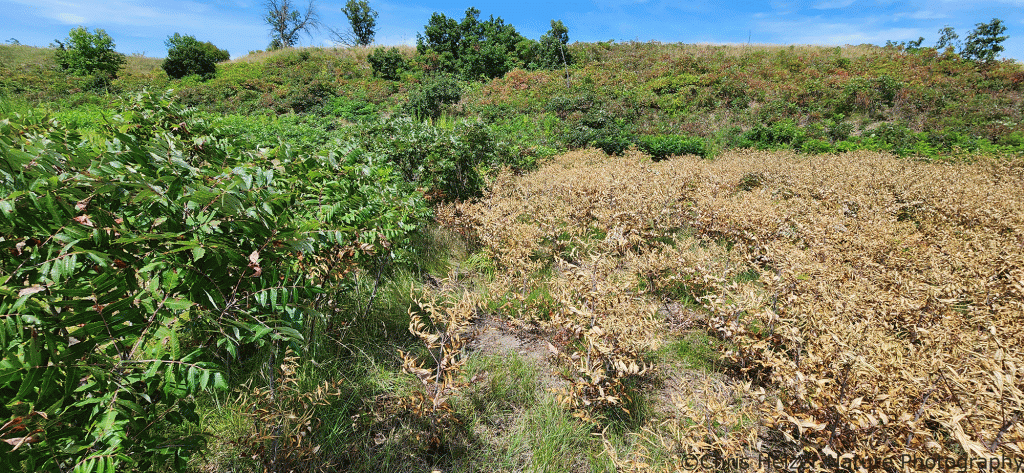
As we’d hoped, we saw no mortality of sumac or any other plants from the herbicide treatment. Instead, it seemed to act much like a prescribed fire, in that it just injured the shrubs. We’d expected it to do some temporary damage to surrounding vegetation as well, but saw very little evidence of that.
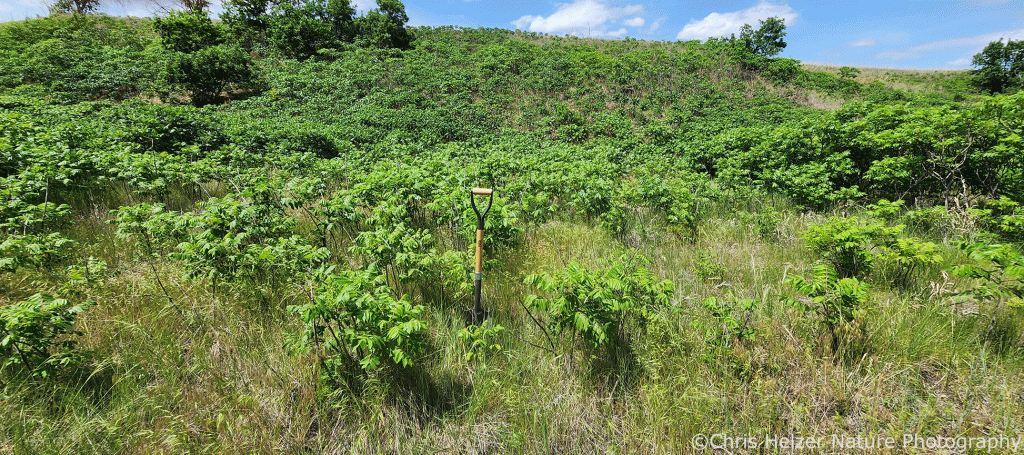
My takeaway from the herbicide application was that it is worth more testing, but seems less effective than mowing or fire. In places/situations where spraying might be feasible, but mowing isn’t, it might be a decent follow-up treatment to extend the impacts of prescribed fire. Maybe. We’ll see. Either way, it didn’t seem to cause any damage to the plant community around the sumac, which reinforces my interest in more experimentation.
.
Field Trial #2 – Rough-Leaved Dogwood at The Nature Conservancy’s Platte River Prairies
For a few years now, I’ve been paying attention to fenceline differences and other evidence that cattle grazing has potential to help manage deciduous shrub height and density. This spring (2024) we set up a quick experiment to test that with rough-leaved dogwood. Cattle were brought into the unit in early June and will be present through October (part of our larger open gate grazing experiment.)
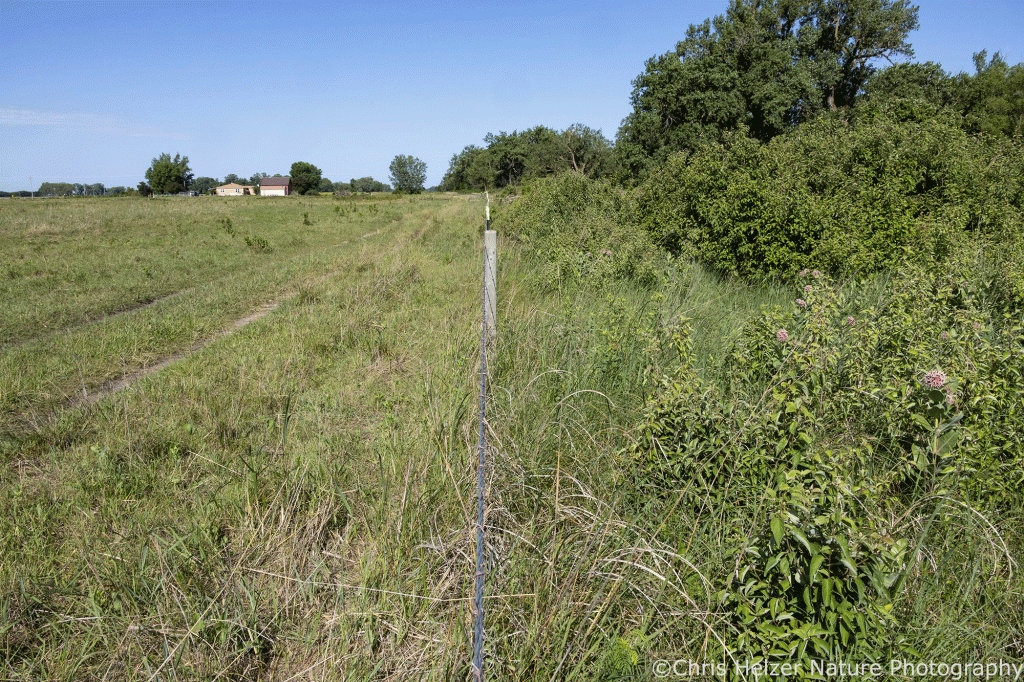
Forty cow/calf pairs were introduced to a 49 acre pasture in late May, 2025. In early July, they were given another 25 acres (in addition to the initial 49) and later this summer, they’ll gain access to an additional 69 acres. The photos below, though, were all taken on June 10 – about 2 weeks after cattle were brought into the pasture. In other words, the grazing impacts shown below happened pretty quickly after cattle were brought in. It’s not like they waited to graze dogwood leaves until they’d eaten everything else.
We set up four treatments:
- Grazed (unmowed)
- Ungrazed (unmowed)
- Mowed/Grazed
- Mowed/Ungrazed
The height of all dogwood stems included in the study was measured on April 22, 2025 and some of those stems were mowed immediately afterward. Small exclosures were set up to exclude grazing from some treatments.
Quick summary of preliminary results (as of June 16, 2025):
- Cattle are definitely grazing the leaves of dogwood. Stems outside the exclosures looked very ragged compared to ungrazed plants.
- Dogwood stems mowed in April were being kept cropped off at just a few inches in height.
- Dogwood stems mowed in April but excluded from grazing had already reached about 10-12 inches in height by June 16.



This project is just getting started, but it’s gratifying to see that cattle are grazing dogwood as we’d expected (see photos below for further confirmation). The most promising result so far is that the mowed dogwoods seem particularly attractive to cattle and we hope repeated grazing of those resprouting stems will lead to several years of much-reduced growth compared to stems in the other treatments. Time will tell, but we’re off to a good start.
My real hope is that we can find ways that cattle grazing can play into our larger efforts to manage shrub height and density. For example, burning every 4-5 years isn’t enough on its own to suppress shrub growth. However, burning followed by a season of grazing on the regrowth of those shrubs might lead to significantly reduced growth over the next several years. By the time the next fire comes through, those shrubs might not have grown very tall at all.
We have lots of experience (and data) showing that some kinds of cattle grazing can benefit habitat heterogeneity without reducing plant diversity. If similar grazing approaches can also suppress the height and density of shrubs, that’ll be a huge help.
This (including the sumac work above) is just the start of a long experimental path, but I’m excited by the early results.

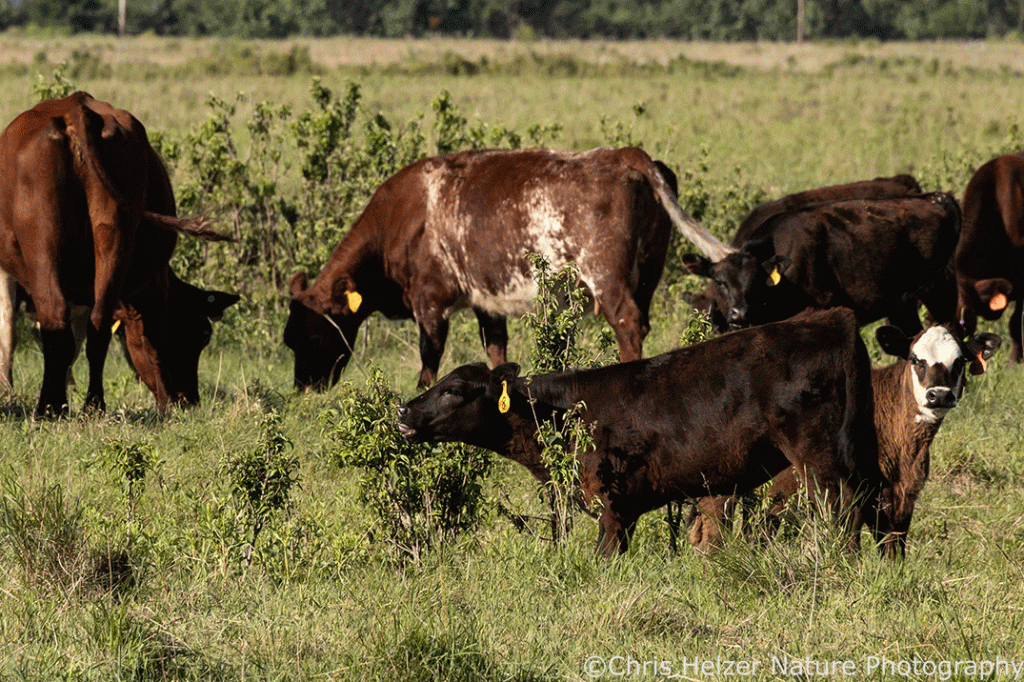
I’m sharing these very early results in the hope that I can encourage others to do similar experimentation. Please don’t interpret these preliminary findings as anything more than what they are. We’re seeing some hopeful signs, but need to follow these trials for more years to see the longer-term impacts of what we’re trying. We also need to greatly expand the treatments and combinations to really understand what various options can do.
Please help! If you are a land manager in the Central U.S. and have shrubs in your grassland, it would be terrific if you could test these or similar approaches to managing shrub height and density and report back. Just as importantly, we need researchers to help us learn about the impacts of different degrees of shrub height and density on plant communities, pollinators and other invertebrates, birds, mammals, and much more. That information will be crucial to land management and help tell us what to aim for.
As I said in the first post, the increase in woody plants in our grasslands doesn’t have to be a catastrophe. It might just be one more factor we need to include in the way we think about managing prairies for various objectives. If we ignore the issue until the shrubs have filled in and taken over, though, we’ll definitely lose. Let’s not lose, ok?