This was a really fun week, but it was one jam packed with social interactions. The America’s Grasslands Conference happened just down the road and I gave a few presentations and several tours associated (officially and unofficially) with that. I also had a great time meeting new people and catching up with old ones. By the end of Thursday, though, my social engine was pretty much out of gas (I should probably think about upgrading to a more eco-friendly social engine).
As a result, on Friday morning, I got up and drove down to our family prairie to catch sunrise. I spent most of my time in the 80×80 foot plot there tied to the post-grazing photography project I’m doing this year. It was just the thing to reinvigorate me.

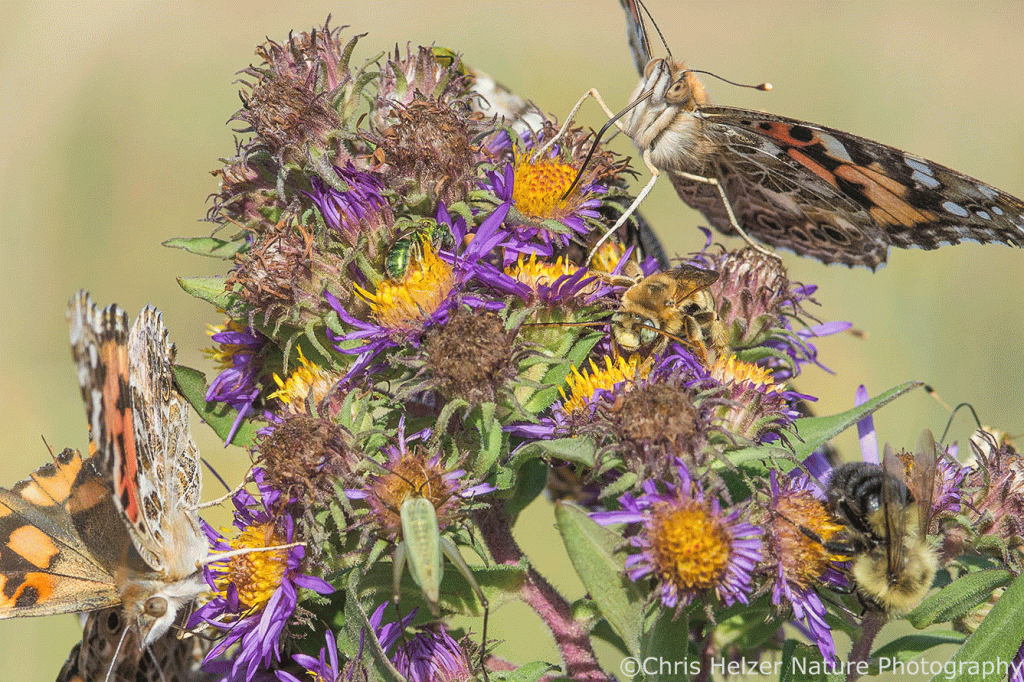
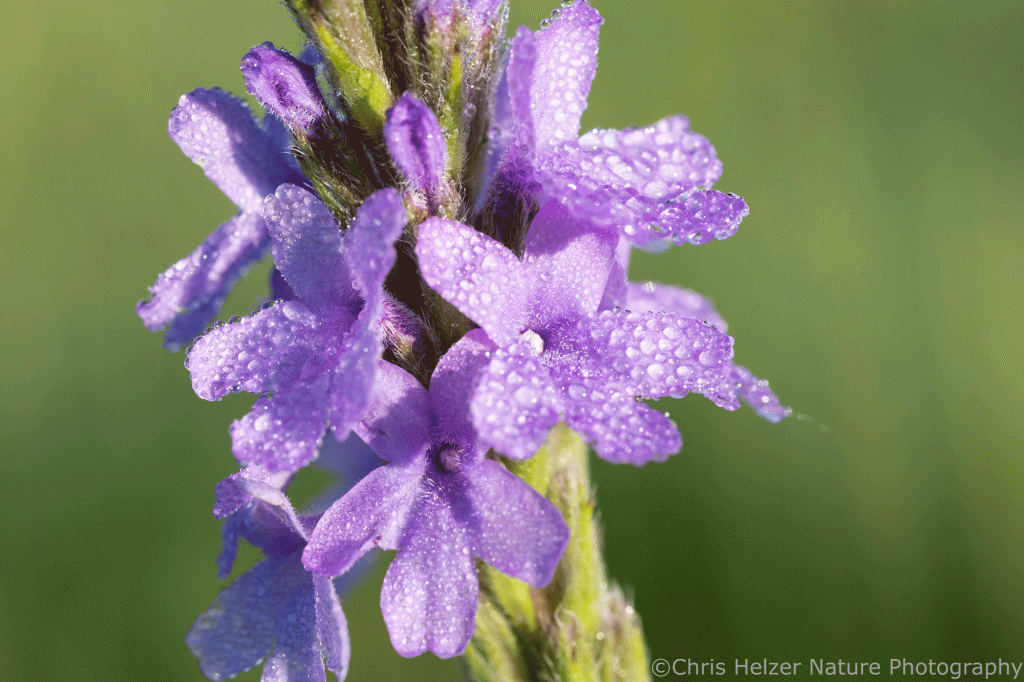
The prairie was full of life and activity, even on a dewy morning. Purple prairie clover is starting to bloom across my project area, adding a lot of color, but also drawing a lot of attention from various invertebrates (more on that below). Yarrow, flax, and daisy fleabane were still in flower, but obviously on the back end of their blooming period. Upright prairie coneflower, hoary vervain, and other wildflowers were also joining the party.


We’ve had good rains lately, so there were mushrooms around, including on manure piles. I was surprised to see what I think are the same species on manure from last season as well as from this season (in areas outside of my photography project area). I guess I’d expected to see mushrooms on fresh dung, but not necessarily on older piles. Or that maybe that the fungal species would differ between young and old piles. I’m not really sure why I thought that, but either way, I was wrong. Look at me – learning new things!

Back to the prairie clover, I saw a few crab spiders hanging around on them, and some drone flies had shaken off the dew and were making the rounds looking for pollen. I only saw one bee, but I assume that’s because the others were waiting for the dew to dry – prairie clover is usually one of the top bee-attracting wildflowers in our prairie when it’s blooming. I’ll go back soon and see what’s happening when the whole prairie isn’t soaking wet.
What I saw most on those prairie clover flowers were little katydid nymphs. They were ubiquitous. Tiny, long-antennaed, grasshopper-like creatures were hanging out and (I think) feeding on the pollen and/or anthers of many of the flowers. (I just had to convince my computer that “antennaed” is a word. It keeps underlining it to highlight the fact that it doesn’t think it’s correct. I even looked up the word to make sure I wasn’t the crazy one. What’s funny, of course, is that I looked it up online, which is a skill you’d think my computer would also have.)
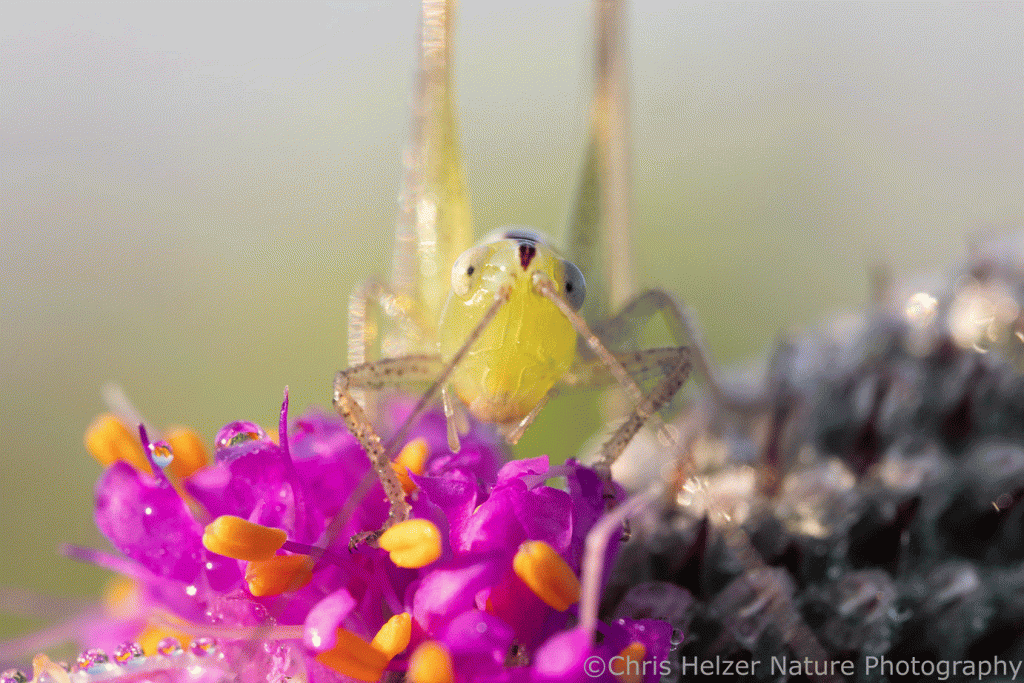
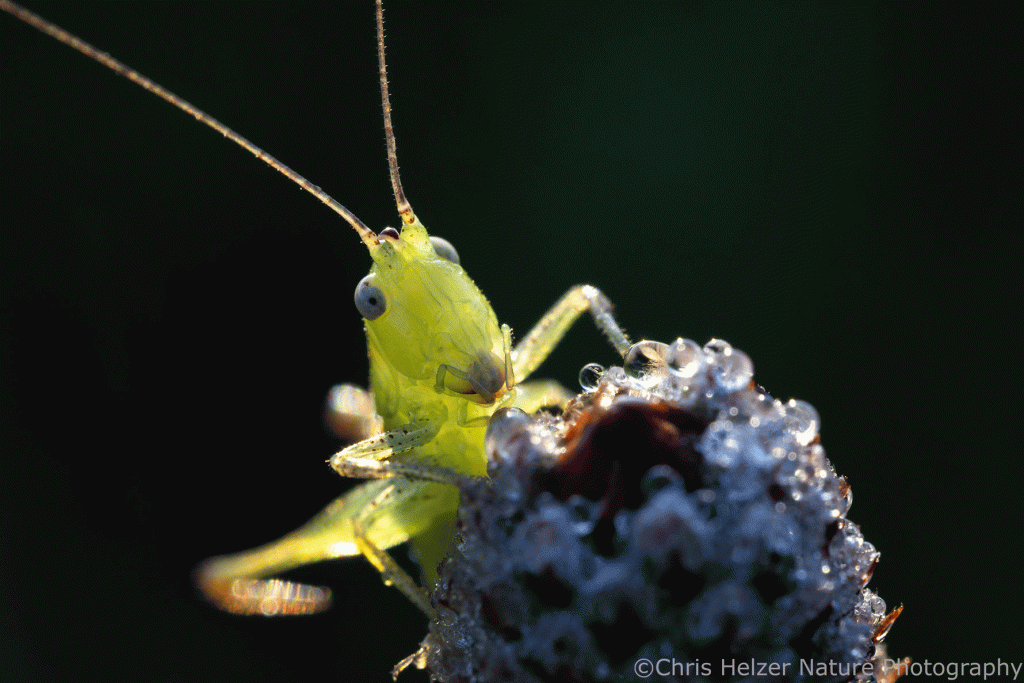
Most of the tiny katydid nymphs were only about 1/4 inch long, but their antennae were several times longer than their bodies. As I’ve done countless times before, I wondered how they managed to move around in the prairie with those things sticking out like that. You’d think they’d get hung up in the vegetation over and over. Can you imagine trying to walk through a forest with 25-foot fiberglass poles stuck to your head? It must be similar. It’s just one more reason to admire katydids, I guess.
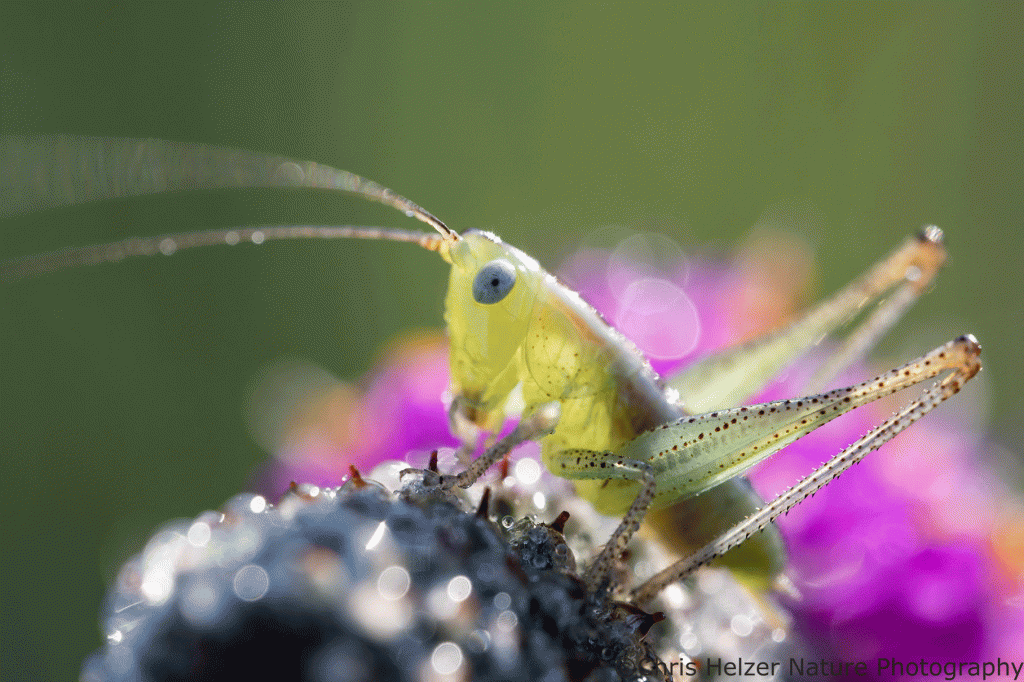

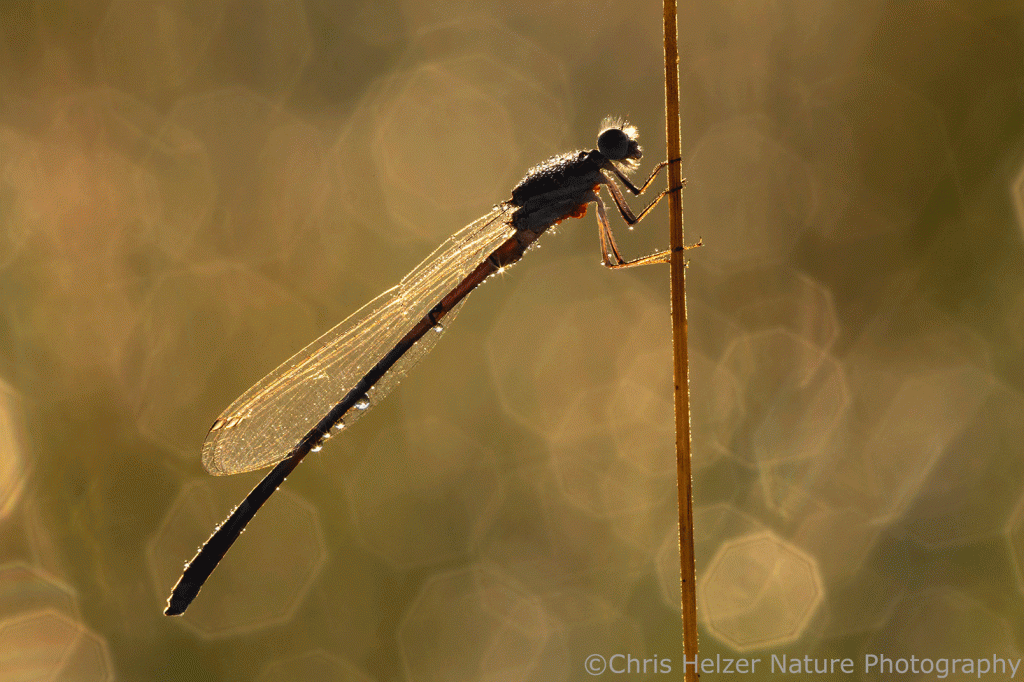
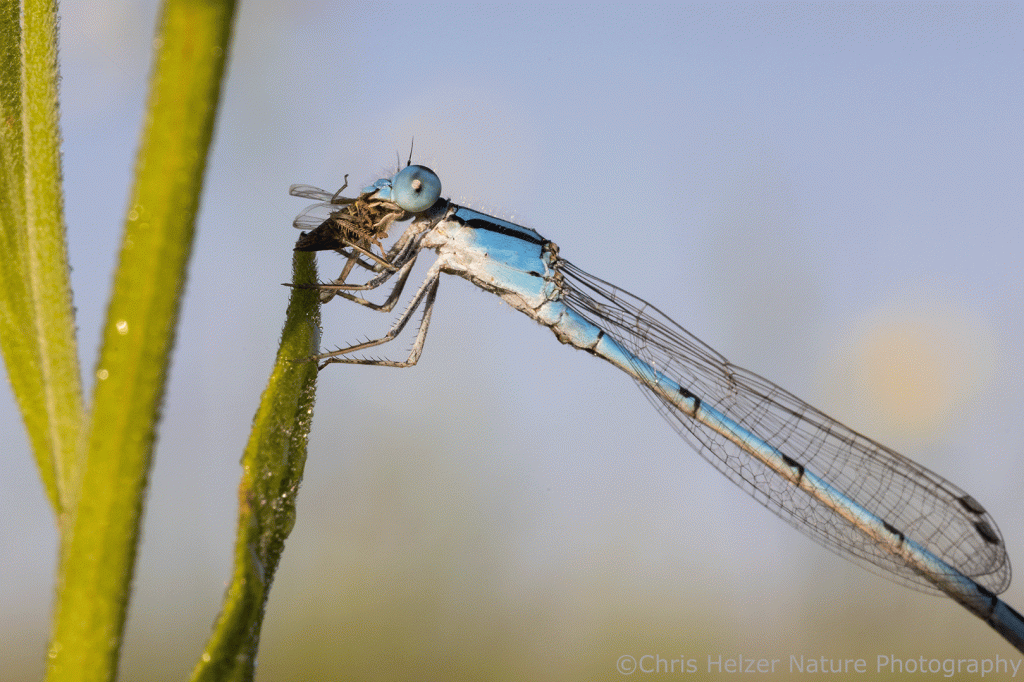
There were lots of other invertebrates around, of course, including ladybirds, grasshoppers (large and small), flies, lynx spiders, wolf spiders, funnel-web spiders, and many others. Damselflies were particularly noticeable as I walked carefully through the vegetation. As I’d step, a few would fly a short distance away from my feet and land again. The only way I could get close enough to photograph them was to lie prone on the ground and army crawl slowly toward them, keeping my head low. Even then, of course, only a few let me get close. One of them was distracted (I assume) by the small insect it was feeding on. I never did figure out what it was eating. Initially, I thought mosquito, but looking at the photos later, I’m not sure.
The biggest highlight of the morning was seeing purple coneflower in bloom. This is a species that I’ve only seen a few times at my family prairie, and never in this particular location.

A couple weeks ago, I spotted two different individuals of purple coneflower and it looked like both were going to bloom. One of them was doing just that on Friday morning, with three flowers in various stages of opening. The mystery now is whether those plants have been hiding there for many years and I just noticed them this year or whether they came in from seed.
I’ve been overseeding the site every year for the last 15 years or so – tossing seed out in the winter where cattle had grazed hardest the previous season. It’s been a slow, gradual process because I don’t have a ton of time to harvest seed. I know I’ve had some purple coneflower in my mix a few times over the years, but definitely not within the last 4-5 years. Either way, it’s pretty fun that the first time I’ve seen them bloom is the year AFTER their part of the prairie experienced a year and a half of heavy grazing (the last half of the 2023 growing season and all of the 2024 season).

After a couple hours of exploring the prairie, I left for home feeling much better. That happens after walking any grassland, but the feelings are especially strong after I leave a prairie with which I have a strong connection.
At work, I have built lots of prairie from the ground up (both harvesting and planting the seed – with help from others, of course). Our family prairie has been under my management for about 20 years now, counting the years I helped my grandmother when she was still around. In both cases, the emotions that come with those personal ties are awfully profound. I know that every plant, every insect, every bird, skunk, mushroom, or other organism I see in those places is responding to a chain of events I helped put in motion through my restoration and/or stewardship work.
I mean – wow. Just wow.