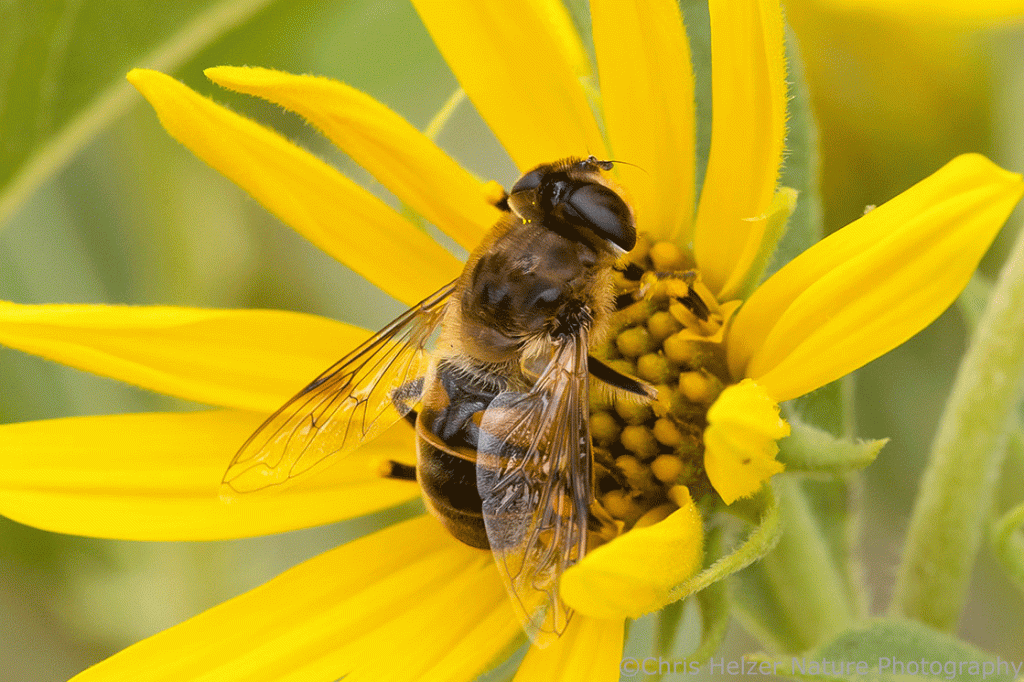
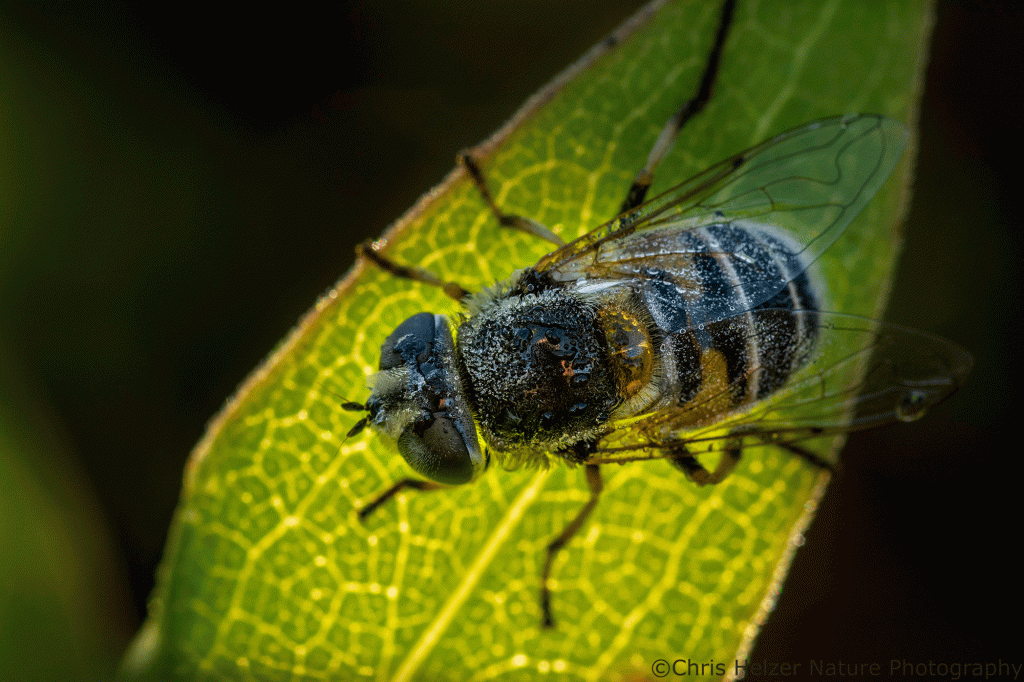
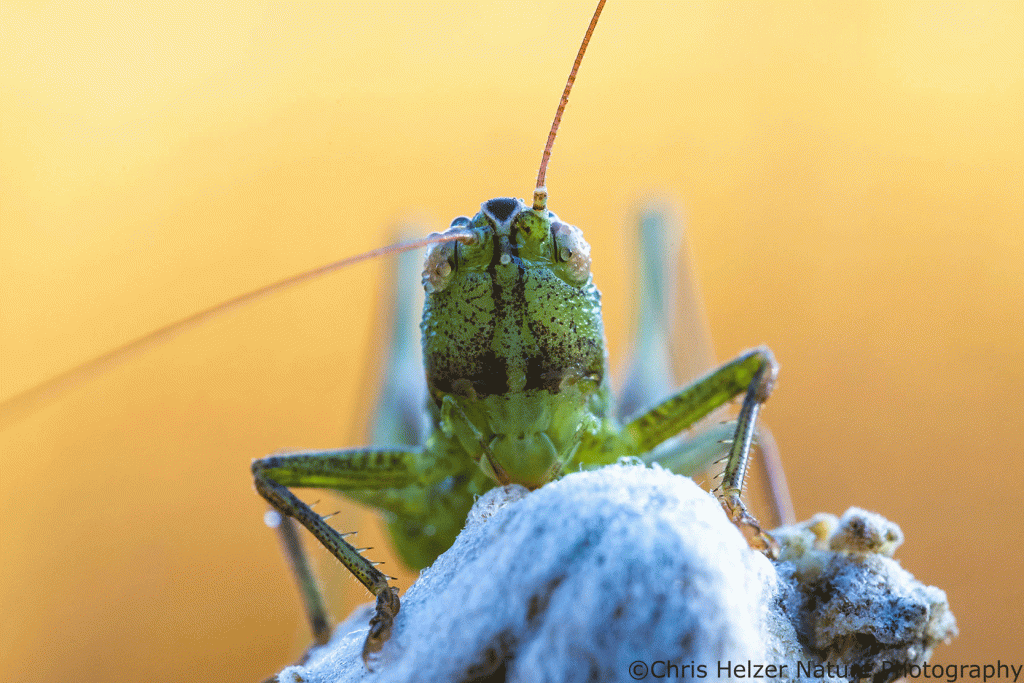
The fall migration is in full swing through our prairies. Dragonflies, birds, butterflies, and more are moving southward. Going out on dewy mornings is a great way to check up on butterflies and dragonflies because I can find them immobile and covered in dew on their overnight roosts. This week was a big week for variegated meadowhawks (dragonflies), apparently. I found dozens of them at our family prairie one morning (more photos toward the end of this post).

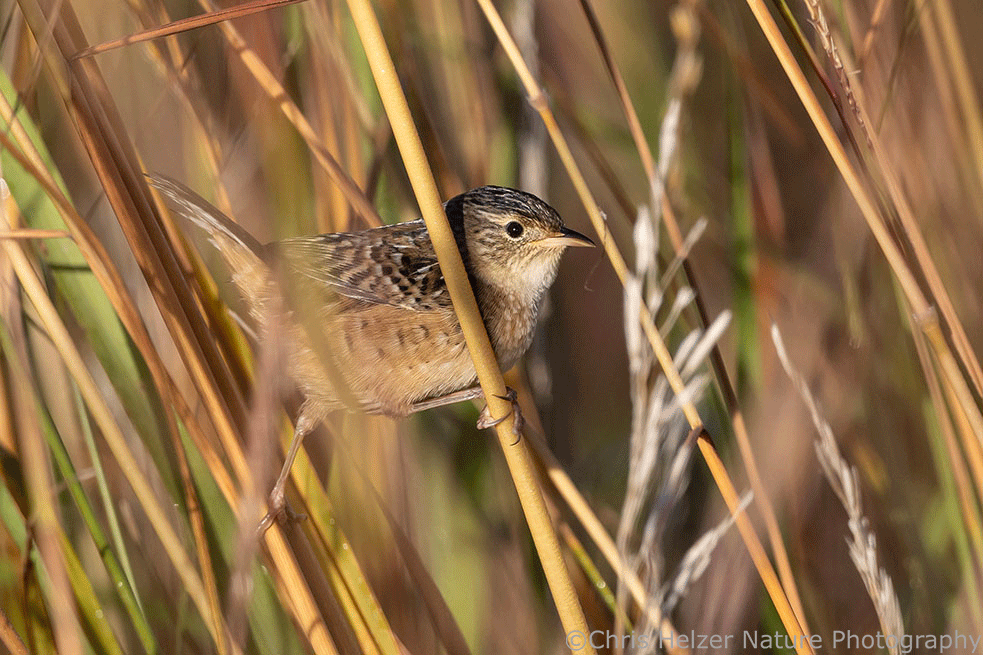
There are lots of little brown birds skulking in the vegetation this week. Many of them are grassland sparrows of various species, but there also were a bunch of sedge wrens at our family prairie. Most of those birds are hard to see unless you flush them while walking through the prairie, but just standing still is also a good way to hear them as they rustle around in patches of tall grass. The sedge wrens made it easy because they not only rustled, they also called to each other with their machine gun songs (“Dot Dot d-d-d-d-d-d-d-d-d-d!”).
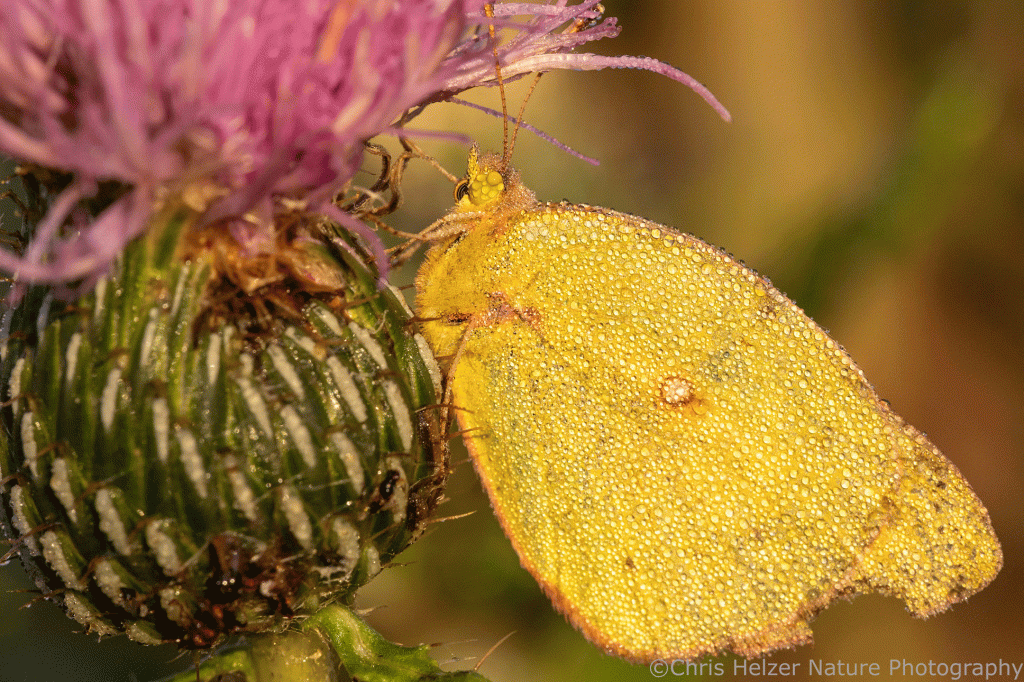
Monarchs are far from the only migratory butterfly (not to mention moths) coming through. I’ve seen a lot of painted lady butterflies this week and found a few orange sulphurs that (probably?) were on the move. There was a cluster of pearl crescent butterflies in our yard this week, too, but as far as I know, those aren’t migratory. They looked like they’d all recently emerged as adults, so they’d better hurry if they’re going to lay eggs before freezing temperatures hit!
As I see the abundance of flies still active at this time of year, I can’t help wondering how many of them are migrants. A year ago, I wrote a post complaining about the lack of North American research on migratory flies. I’m sure that spurred a flurry of activity among researchers (eye roll) and that we’ll soon know a lot more about the topic. In the meantime, I’m left to wonder, especially about all the different drone flies and hover flies I see. Are they just scrambling to eat (and lay eggs?) before frost? Or are they fueling up during a long southward journey?

Most insects, of course, don’t migrate, so they have to survive Nebraska winters however they can. That usually involves finding a sheltered place to hide and then just withstanding freezing conditions. Species vary in terms of whether they go through winter as adults, eggs, or larvae/nymphs. All of those options seem to work ok.

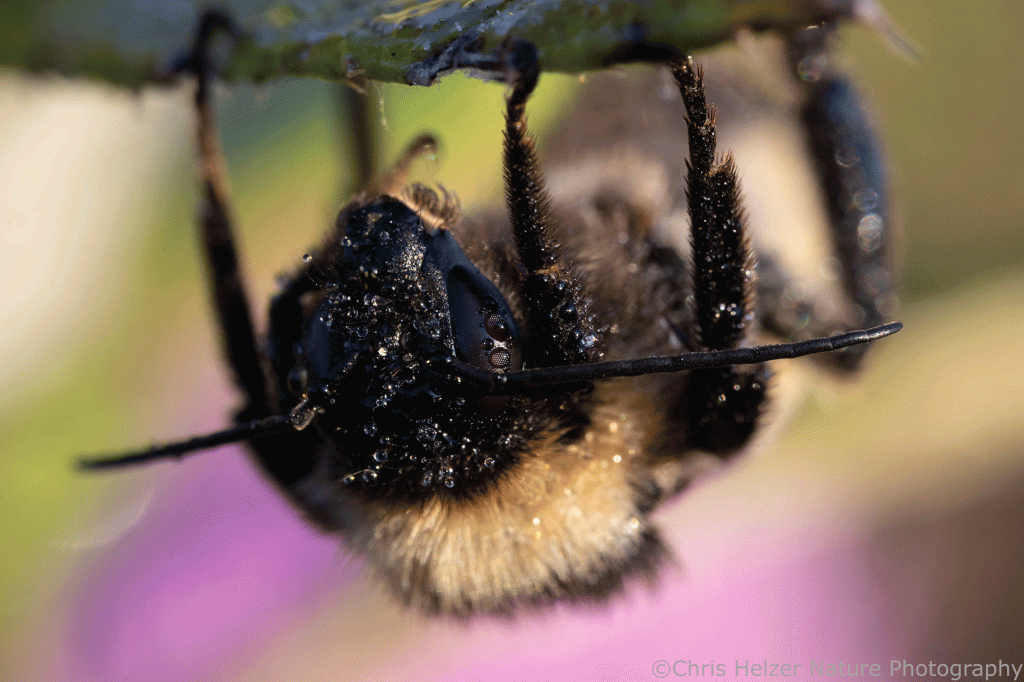
A lot of the individual insects out and around now will simply die as winter hits. The only bumblebees, for example, that survive the winter are the fertilized females that will be next year’s queens. Everyone else in the colony will perish at the end of this season. Other insects that lay eggs before winter will also die after completing that task. I imagine that abundance of dead insects provides a big bonanza of food for any animals out poking around after the first big freeze or two. If not, bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms will clean up the rest.

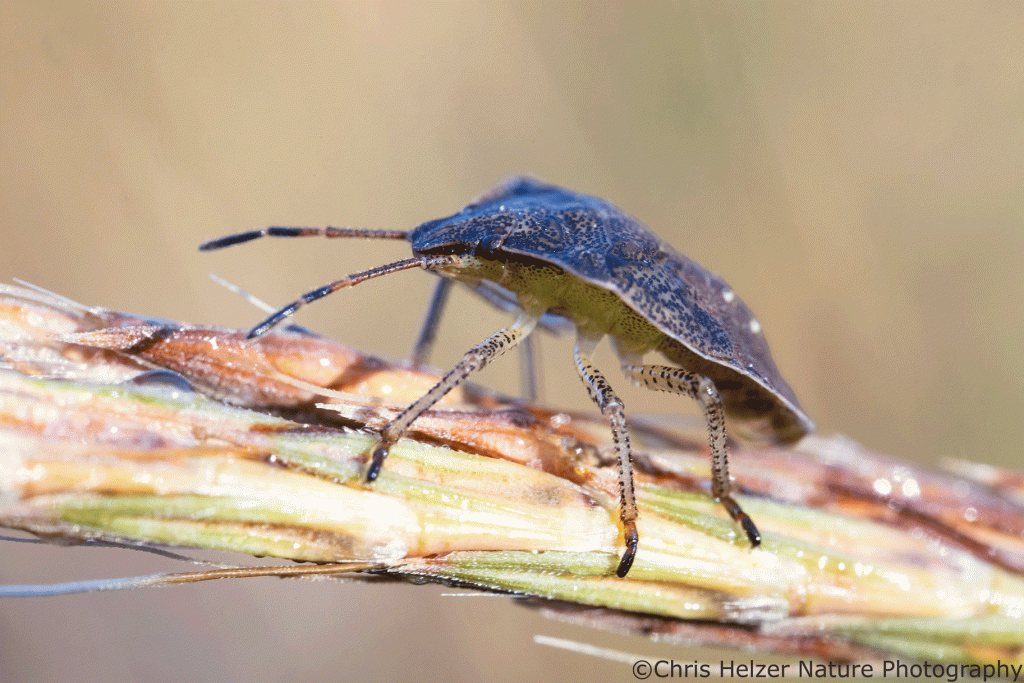
Plants are also shutting down for the year. Most wildflowers and grasses are finished blooming and have produced seeds if they can. Perennial prairie plants are also making buds. Woody plants make buds aboveground where new leaves or stems will emerge next year so the plants can continue to grow larger (assuming they don’t get burned, chewed, or cut down). Herbaceous plants, though, including grasses, wildflowers, and sedges, create buds at their bases, usually right below the surface of the soil.
Over the winter, the entire aboveground portion of perennial herbaceous plants dies back. In the spring, though, those plants will start a new season of growth from their basal buds. Seeds are still important for those perennials, though, both because it allows them to combine DNA with others of their species (cross-pollination) and because it lets them spread progeny into new places. Seed dispersal strategies are fascinating and beautiful, and it’s a fun time of year to see a lot of them in action.


Late summer and early fall are great times for dewy mornings. Those water droplets are a boon for insect photographers, but they also make nice photo subjects on their own.


Back to the abundance of variegated meadowhawks this week… I can’t remember seeing so many at a time before, but that doesn’t mean much. I tried to quickly photograph a selection of those I found at our family prairie one morning, but I just kept finding more and more. Here are the ones I managed to photograph:
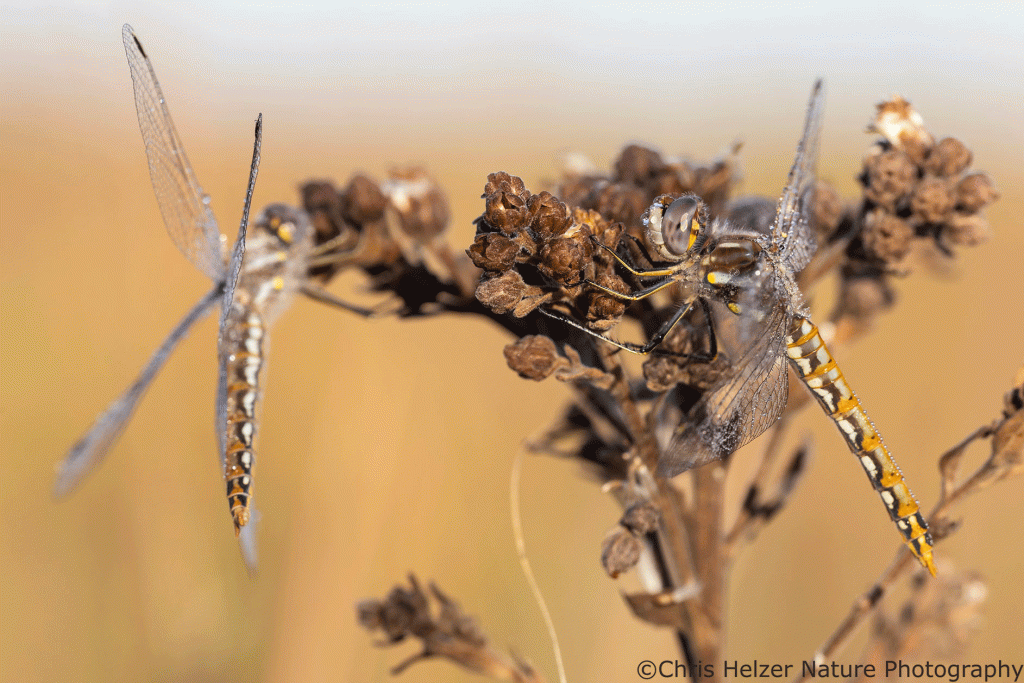


There was one dragonfly in particular that was perched attractively on top of some stiff goldenrod as the sun came up. I circled back to it a couple times as it started warming up and managed to photograph it from multiple angles while it was still too cold and wet to fly away. All the rest of the photos below are of that same individual.


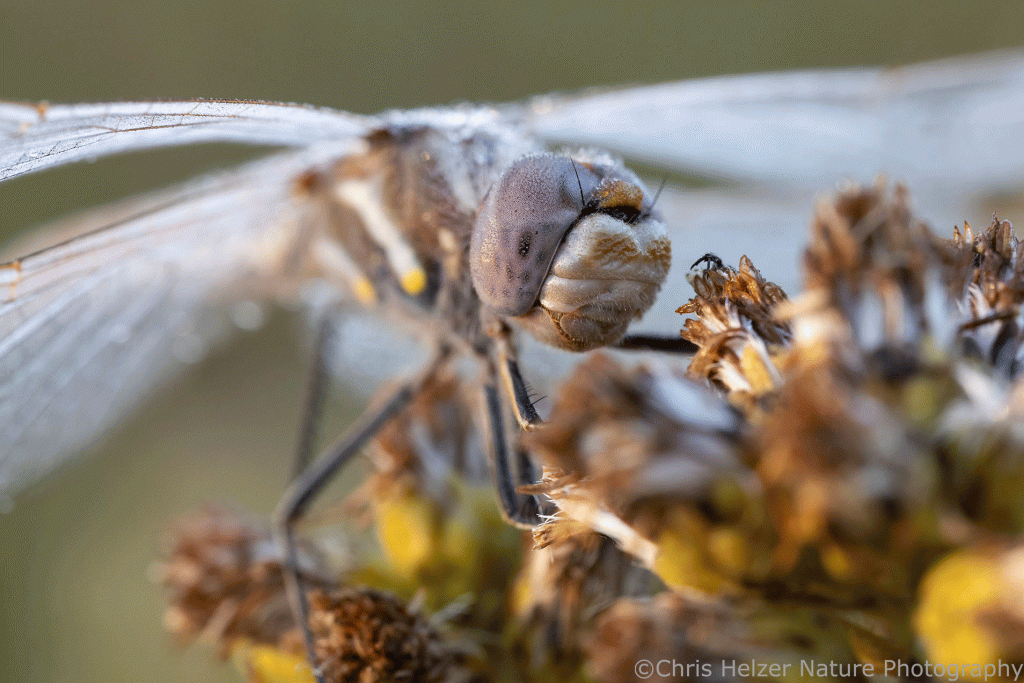


I don’t know how much longer this late season flurry of activity will last, so I’m trying to catch as much of it as I can. I’ve gotten behind on some projects because I’m trying to see things before they’re gone, but I’ll have the whole winter to catch up, right?