Life is funny sometimes. Last week, I spent a morning setting up some research plots aimed at helping us learn how to suppress the growth and spread of deciduous shrubs in grasslands. When I finished, I walked about 50 yards to a patch of wild plum (a deciduous shrub) and spent a half hour photographing an incredible abundance of pollinators using the patch as a source of food. Really makes you think, huh?


Deciduous shrubs, of course, are great. Wild plum, for example, is one of several early-blooming native shrubs that play a vital role for pollinators in April. There aren’t a lot of blossoms among the herbaceous prairie plants in our area at this time of year. As a result, blooming shrubs draw insects in like big, showy, nice-smelling magnets. Aside from their pretty, nutritious flowers, shrubs also create nice little pockets of habitat for a lot of animals that need a little woody cover with their prairie vegetation.
On the other hand, deciduous shrubs have been spreading into and through grasslands at an increased rate. That rate of spread is caused by a lot of factors, including changes in native browser populations and a style of landscape fragmentation that has broken grasslands into pieces and introduced woody plants along the edges of those pieces. Most importantly, higher levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are fueling the growth and spread of deciduous woody plants in a way that is very different than even a couple decades ago.
Adding all that up, it can be hard to know how to feel about and act around deciduous shrubs in prairies. Shrubs yay? Shrubs boo? Yes.



I was only able to photograph a tiny fraction of the pollinator species frenetically bouncing between the plum blossoms. Many were so tiny, it was hard to photograph them at all, and most were moving so quickly, I couldn’t focus my lens before they skipped off to the next flower. Even so, I managed to capture a decent sample of the kind of diversity I was seeing. You’ll just have to imagine the others.

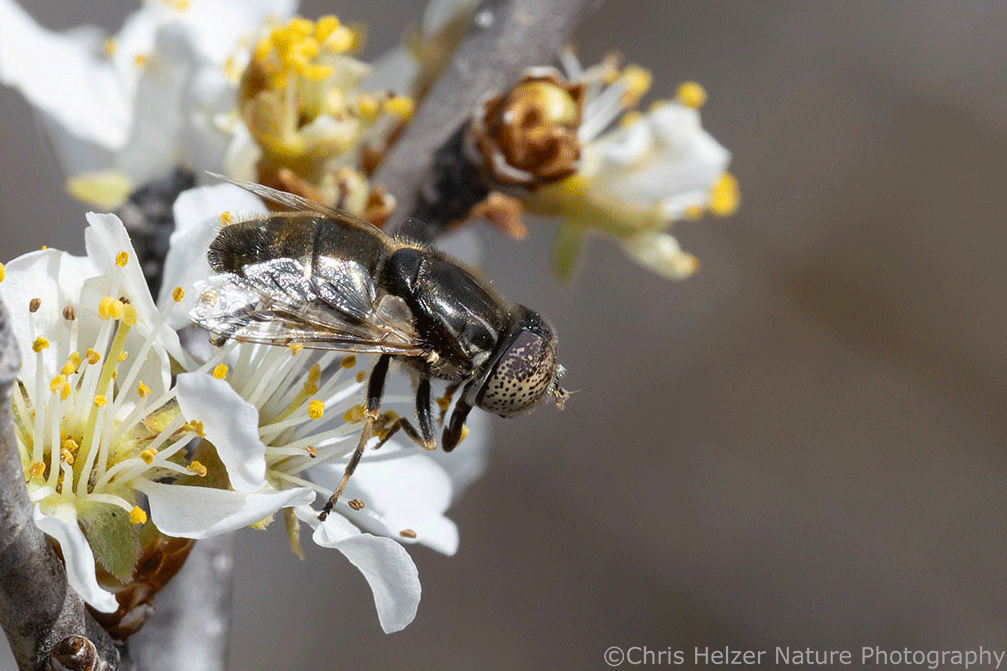

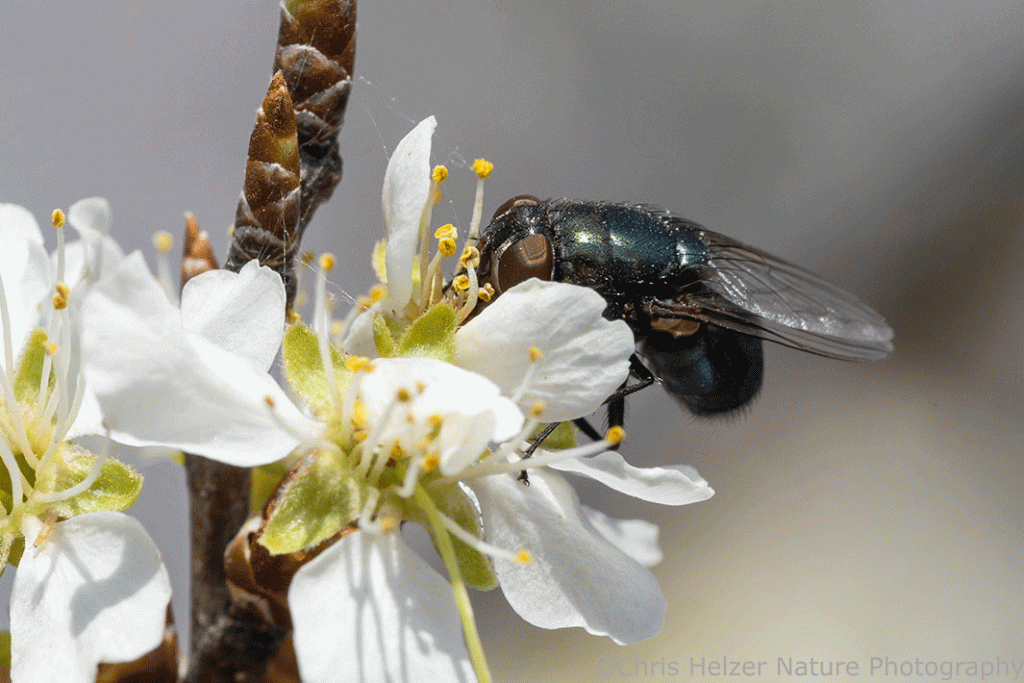
Managing the size and spread of deciduous shrub patches is already a major focus of many prairie managers. The challenge of dealing with that issue is growing like – well, like a patch of carbon dioxide-fueled deciduous shrubs. Most of the shrub species we’re facing, though, aren’t enemies. As with the wild plum I was photographing, the majority are native species that happen to be gaining a competitive edge because of a number of enabling conditions we can’t do much about.
As land stewards, we need to find ways to manage shrubbier grasslands for biodiversity and productivity because shrubbier grasslands are our future across much of the Midwest and Great Plains regions of North America. In fact, the future is already here in many places. We’re all free to think what we want of that future, but ignoring or denying it won’t do us much good.
But they’re also pretty! And they provide a lot of pollen, nectar, fruit, shelter, and other resources for prairie species.
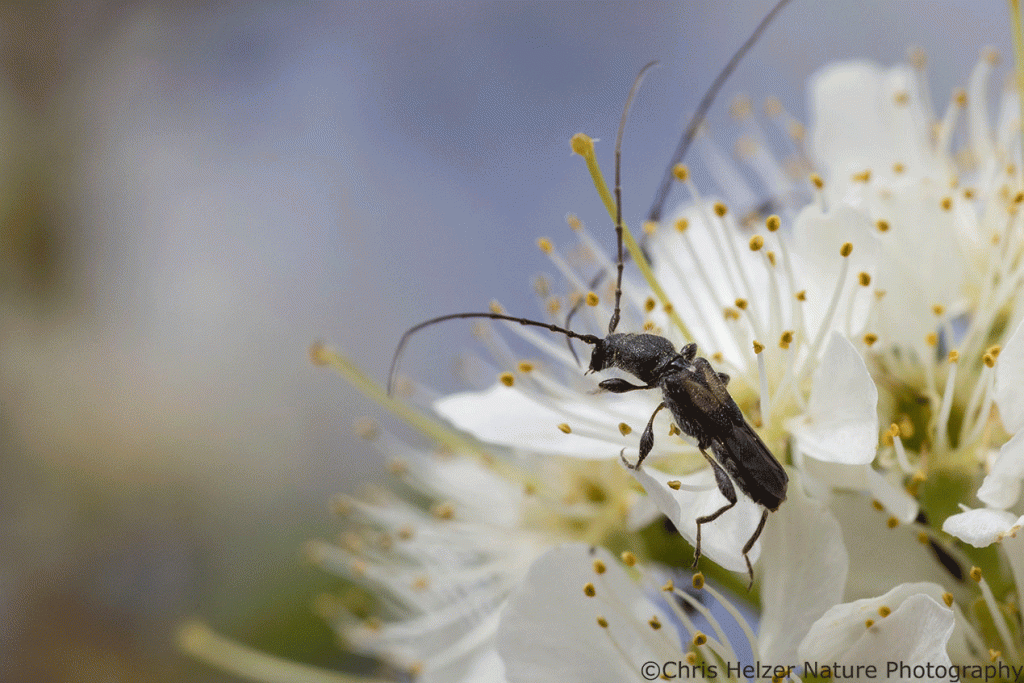
Really, the dual experiences I had with shrubs last week were a great illustration of how we should all be thinking about them. We have a lot to learn, and quickly, about how to manage the competition between shrubs and other prairie species. As we experiment with various approaches to the issue, we need to share our experiences with each other. At the same time, we should all recognize and celebrate the positive traits of those shrubs. That’ll help us make better decisions, but it’ll also give us a helpful perspective on the changes we see around us.
Happy Earth Day.









